" Programming is similar to a game of golf. The point is not getting the ball in the hole but how many strokes it takes. " - Harlan Mills
The quote above means that, it is not a bout how many lines to do a program. If you did a program in one code line and someone else did it with 3 codes lines, then your program is better, because you consumed time, and memory from your computer. If you can make the same program with less codes then this is the smart way to do it, even when you fix it, it will take less time. And that's go to our lives too, if we can do things with less time, money and effort then we get the same result, aren't we going to take that path?

I tried this code above around 7 times till I got it right and print a result on the screen. It drove me nuts !! so don't be shocked if you faced the same thing.
Let me explain it to have a better picture.
First of all, you need to define the value of the function under the Sub Main, if you didn't then you wont have anything print of the screen. As I explained in previous lessons that Dim means Dimension, As Integer is type of data ( identify numbers ) and " = CalculateSum(3, 4)" are the numbers we want their value to return to us.
As I saw many examples on the internet and tried different codes, I figured that you need to write the function this way:
Function Sum(ByVal A As [ type of data ], ByVal B As [ type of data ] )
Like above example:
Function CalculateSum(ByVal A As Integer, ByVal B As Integer) As Integer
Write the Keyword " Function " then name it anything like " CalculateSum" , ByVal A or Car or Apple, anything you want; it is just a name. Then do the same thing after the comma.
Dim result ( or any message you want ) As [ any data type ] = ( the value you want ). By writing " Return message, or result or any name you put after the Dim word" , then the compiler will know to keep the value and return it to us ( to the Main ). End the function and run the program. The value returned by a function called result or returned value.
Let's jump to a different topic. Remember the first example I gave you about HelloWorld? Eric and Sandra? Well, we are back to it now and we will change the way we greeted Sandra and Eric. Let's re-write the correct function and add " If, Else " statement.
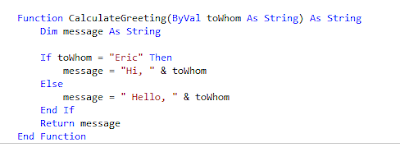
When we used the If statement, we were testing the value of toWhom. If toWhom is equal to Eric then the value returns one greeting and it will be like below picture.
In the If statement, the program compares the value toWhom variable against the string "Eric". So if you want to test two values to see if they are equal, you use equality operator.
There is other comparison operators in VB:
= : Equality. The expression has the value true when the left and right hand values are true.
<> : Inequality. The expression has the value true when the left hand is not equal to the right hand.
< : Less than. The expression has the value true when the left hand value has less value than the right hand value.
> : Greater than. The expression has the value true when the left hand value is greater than the right hand value.
<= : Less than or equal. The expression has the value true when the left hand value is less or equal to the right hand value.
>= : Greater than or equal. The expression has the value true when the left hand value is greater than or equal to the right hand value.
So let's say toWhom= " Eric " , then when the expression will work out, it will evaluated True, because right hand and left hand values are equal. If toWhom has other values then the expression will evaluate False. Boolean Expressions are the expressions that evaluate True or False value.
This what we should know for Functions and controlling your program. The next lesson will be about Looping and Iteration, those two things are also included on how your program should flow.

No comments:
Post a Comment